Gesture-controlled music generation
This prototype targets the creation of interactive generative music experiences based on Interactive Machine Learning (IML)-based gesture recognition.
Interactive Machine Learning refers to the use of machine learning algorithms to design by interactively providing examples of interaction. This “embodied” form of design taps into our natural human understanding of movement which is itself embodied and implicit. We are able to move and recognize movement effectively but less able to analyze it into components. IML allows designers to design by moving rather than by analyzing movement. For more details check out Rebecca Fiebrink’s PhD thesis on the subject.
IML has been used in sound and music related interactive projects many times. It is usually used to recognize and map user input in form of gestures and poses into parameters of the sound. Wekinator is widely used to recognize discrete user poses and map them into values that be interpolated from the given examples. Gesture Variation Follower is traditionally used to map a single example gesture (poses over time) to a sound, and use the performer variations on the gesture to modify the sound playback. This prototype proposes a third approach, one that maps gestures (poses over time) to (interpolated) parameters, in order to control a music generator.
Gesture-controlled music generation
We use Hierarchical Hidden Markov Models (HHMM) from the XMM library to model the input from the user’s sensors to the parameters. To do so, we first use some chosen parameters to generate music and record the user making gestures and moving on the music. We repeat this for every set of parameters, each one with a different gesture. We then train the model. At the end the user can make gestures and parameters will be generated to control the music. If the gestures match the trained ones, the parameters will be the ones used to train the model. New sets of parameters, interpolated from the ones used for training will be generated in case on non-matching gestures.
The music generation process is carried out using prototypes from the GiantSteps project.
We used the r-IoT sensor module to sense the accelerations of the user. Those are sent through OSC to a Pure Data patch. This patch uses XMM through its Python interface and the Pd python external. The same patch controls Pd patches through OSC. Both music generator patches send MIDI to a VST.

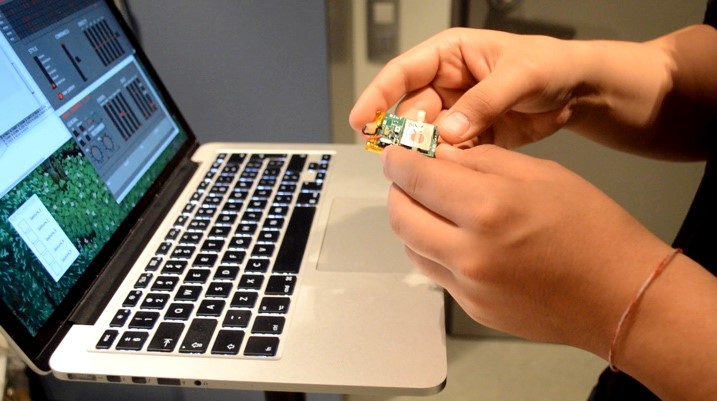
This prototype was created as part of the RAPID-MIX EU project in the Music Technology Group of Universitat Pompeu Fabra. It was eventually incorporated into an awesome product by Reactable Systems called SNAP.